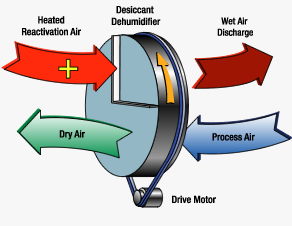
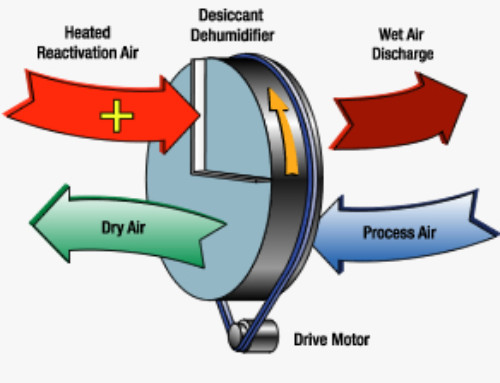
Courtesy of Pottorff:
Absorption Coefficient (1) Ideally, the randomly incident sound power which is absorbed (or otherwise, not reflected) by a material. (2) A measure of the sound absorptive property of a material as approximated by ASTM C 423.
Acoustics (1) The science of sound, including its production, transmission, reception and effects. (2) Of a room, those qualities that together determine the room character with respect to human auditory perception.
Ambient Noise The all-encompassing noise associated with a given environment at a specified time, being usually composite of sound from many sources, at many directions, near and far, including the specific sound source(s) of interest.
Anechoic Room (free-field room) A room whose boundaries absorb practically all the sound incident thereon, thereby providing essentially free-field conditions.
Audible Sound (1) Acoustic oscillations of such a character as to be capable of exciting the sensation of hearing. (2) Sensation of hearing excited by sound waves.
A-Weighted Sound Level The sound level obtained by use of A-weighting. Unit: Decibel. Unit symbol: dB. Often, the unit symbol is followed by a letter A in parentheses, i.e., dB(A), to indicate the A-Weighting which has been used. Abbr.: AL. Letter symbol: LA.
A-Weighted Sound Power Level Ten times the logarithm to the base 10 of the ratio of a given A-Weighted sound power to the reference sound power of 1 picowatt (PW). Abbr.: APWL. Letter symbol: LW
A weighting system applied by octave-band to actual sound pressure levels. The weighting system is designed to weight by importance the most dangerous levels by octave and allow for more low frequency noise. Low frequency noise has not been proven to cause hearing loss as fast as mid and high frequency noise.
Background Noise The total noise from all sources other than a particular sound that is of interest (e,g., other than the sound being measured or other than the speech or music being listened to.)
Band A segment of the frequency spectrum.
Band Sound Pressure Level The sound pressure level within a specified frequency band. The band is usually specified by its geometric center frequency and bandwidth, but it also may be specified by its upper and lower cutoff frequencies. The width of the frequency band may be indicated by a modifier such as octave-band (sound pressure) level, one-third-octave-band level, etc. Bel A unit of level of which denotes the ratio between two quantities proportional to power; the number of bets corresponding to this ratio is the logarithm to the base of this ratio.
C-Weighted Sound Level The sound level obtained by use of C-Weighting. Unit: Decibel. Unit symbol: dB. Often, the unit symbol is followed by the letter C in parentheses, ie., dB(C}, to indicate that C-Weighting has been used. Abbr.: CL. Letter symbol: LC.
Dead Room A room that is characterized by an unusually large amount of sound absorption.
Decibel A unit of level which denotes the ratio between two quantities that are proportional to power; the number of decibels is 1 O times the logarithm (to the base 10) of this ratio. In many sound fields, the sound pressure ratios are not proportional to the corresponding power ratios, but it is common practice to extend the use of the unit to such cases. One decibel is one-tenth of a bel. Unit symbol: dB. dB (PWL) -10 log W/WR where W = 1 x 10-12 watts dB (SPL) -20 log P2/PR where PR= 20 mPa
Direct Sound Sound which reaches a given location in a direct line from the source, without any reflections.
Direct Sound Field That portion of a sound field of a sound source in which the sound pressure level (due to this source) has not undergone any reflection.
Far Field That portion of a sound field of a sound source in which the sound pressure level (due to this sound source) decreases by 6 dB for each doubling of the distance from the source.
Flanking Sound Transmission The transmission of sound from a source room (i.e., a room in which a source is located) to an adjacent receiving room by paths other than the common partition.
Free Field A sound field in a homogeneous isotopic medium whose boundaries exert a negligible influence on the sound waves. In practice, it is a field in which the effects of the boundaries are negligible over the frequency range of interest.
Frequency (1) Of a function periodic in time, the number of times that the quantity repeats itself in 1 second (i.e., number of cycles per second). (2) The reciprocal of the period. Unit: hertz. Unit symbol: Hz. (3) Speed at which pressure varies. F =(speed of sound)(wave length).
Hemi-Anechoic Room A test room with a hard, reflective floor but whose other surfaces absorb essentially all the incident sound incident on them, thereby providing free-field conditions above the reflective plane.
IL or OIL Dynamic Insertion Loss of a sound attenuator, sound barrier, or other element designed to provide sound reduction ina specified frequency band, the decrease in sound power level measured at the location of the receiver when this element is inserted in the transmission path between the sound source and the receiver. Unit: decibel. Unit symbol: dB.
Intensity Acoustical energy per unit area.
Laminar Flow Smooth plane wave airflow (or no turbulence).
Level The logarithm of the ratio of a given quantity to a reference quantity of the same kind. The base of the logarithm, the reference quantity, and the kind of level must be indicated. (The type of level is indicated by the use of a compound term such as sound power level or sound pressure level. The level of the reference quantity remains unchanged whether the chosen quantity is peak, rms, or otherwise).
Live Room A room characterized by a relatively small amount of sound absorption.
Natural Frequency ~ Of a system, the frequency of free oscillation. Nit: hertz. Unit ~ symbol: Hz.
NC (Noise Criteria) A series of curves of octave-band sound spectra in a system for rating the noisiness of an occupied indoor space; an actual octave-band spectrum is compared with this set of curves to determine the NC level of the space.
Noise (1) Any disagreeable or undesired sound or other disturbance; unwanted sound. By extension, any unwanted disturbance within a useful frequency band, such as undesired electric waves in a transmission channel or device. (2) Sound of a general random nature, the spectrum of which does not exhibit clearly defined frequency components.
Noise Reduction Coefficient A single-number rating of the sound absorption properties of a material; it is the arithmetic mean of the sound absorption coefficients at 250, 500, 1000, and 2000 Hz, rounded to the nearest multiple of 0.05. Abbr.: NRC.
NR (Noise Reduction) The difference in sound pressure level between any two points ~ along the path of sound propagation.
Octave The frequency interval between two sounds whose frequency ratio is 2.
Octave Band A band of discrete frequency. Generally defined by the center frequency. Note high bands are wider and include more discrete frequencies than to low bands.
Octave-Band Sound Pressure Level (Octave-Band Sound Level or Octave-Band Level) For an octave frequency band, the sound pressure level of the sound contained within that band. Unit: decibel. Unit symbol: dB. Abbr.: OBSPL. Letter symbol: L 1/1.
Octave-Band Spectrum A spectrum which is one octave in width.
One-Third-Octave-Band Sound Pressure Level For a one-third-octave frequency band, the sound pressure level of the sound contained within that band. Unit: decibel. Unit symbol: dB. Abbr.: TOBSPL. Letter symbol: L 1/3.
Pascal A unit of pressure. Unit symbol: Pa [1 pascal = 1 newton per square meter (1 N/m2)].
Picowatt A unit of power equal to one-millionth of a millionth of a watt (i.e., 10-12 W). Unit symbol: pW.
Pink Noise Noise which has a continuous frequency spectrum and a constant power within a bandwidth proportional to the center frequency of the band. (For example. the power octave bandwidth has a constant bandwidth).
Pitch That attribute of auditory sensation in terms of which sounds may be ordered on a scale extending from low to high. (The pitch of a complex sound depends primarily upon the frequency content of the sound as well as the sound pressure and the waveform.
Pure Tone A sound wave which is a simple sinusoidal function of time.
PWL (Sound Power Level) Ten times the logarithm (to the base 10) of the ratio of a given sound power to the reference sound power of 1 picowatt ( 1 pW; i.e. 10-12W). Unit: decibel. Unit symbol: dB. Letter symbol: Lw.
Random Noise (1) A noise whose magnitude cannot be predicted precisely at any given time. (2) Oscillations due to the aggregate of a large number of elementary disturbances with random occurrences in time. (A random noise whose instantaneous magnitudes occur according to the gaussian distribution is called gaussian random noise)
RC (Room Criteria) A series of curves of octave-band sound spectra in a system for rating the noisiness of an occupied indoor space; an actual octave-band spectrum in compared with this set of curves to determine the RC level of the space.
Receiver A person (or persons) or equipment which is affected by noise.
Reference Sound Power The conventionally selected reference sound power; equal to 1 picowatt (1 pW; i.e., 10-12 W).
Reference Sound Pressure The conventionally selected reference sound pressure; (for air) equal to 20 micropascals (mPa).
Reflected Sound Sound that persists in an enclosed space as a result of repeated reflections or scattering; it does not include sound which travels directly from the source without reflections.
Refraction ( 1) The phenomenon by which the direction of propagation of a sound wave is changed as a result of a spatial variation in the speed of sound. (2) The angular change in direction of a sound wave as it passes obliquely from one medium to another having a different wave velocity.
Resonance Of a system in forced oscillation, a phenomenon such that any change, however small, in the frequency of excitation results in a decrease in the response of the system.
Resonance Frequency The frequency at which resonance occurs. Unit: hertz. Unit symbol: Hz.
Reverberant Sound Field (Reverberant Field) A sound field in an enclosed or partially enclosed space, after the source has stopped, in which sound waves have been reflected repeatedly or continuously from the boundaries.
Reverberation The persistence of sound in an enclosure or partially enclosed space after the source has stopped; the persistence is a result of repeated reflection and/or scattering.
Reverberation Room A room having a long reverberation time, especially designed to make all surfaces as sound-reflective as possible and to make the sound field within it as diffuse as possible.
Reverberation Time A sound enclosure, for a sound of a given frequency or frequency band, the time that is required for the sound pressure level in the enclosure to decrease by 60 dB after the source has stopped. Unit: second. Unit symbol: s. Letter symbol: T 60_.
Room Absorption The total absorption in a room due to objects and surfaces in the room, and of air absorption within the room. Unit: sabin or metric sabin.
SABIN A unit of measure of sound absorption; a measure of the sound absorption of a surface. It is the equivalent of 1ft2 of a perfectly absorptive source; a metric sabin is the equivalent of 1 m2 of a perfectly absorptive surface.
Scattering The irregular diffraction of sound and reflection of sound waves in many directions.
Signal to Noise Level The signal noise minus the noise level, usually in decibels.
SOUND. A physical disturbance in a medium (ie AIR) tha is capable of being detected by the human ear. (2) The hearing sensation excited by a physical disturbance in a medium.
Sound Absorption Coefficient (1) Ideally, the fraction of the randomly incident sound power which is absorbed (or otherwise not reflected) by a meterial. (2) A measure of the sound-absorptive property of a material as approximated by ASTM method C 423. Letter symbol: α
SOUND FIELD. A region of an elastic medium (such as air) containing sound waves.
SOUND INSULATION. The capacity of a structure to prevent sound from reaching a receiver room. Sound energy is not necessarily absorbed; reflection back toward the source is often the principle mechanism.
SOUND INTENSITY. In a specified direction, at a point, the average rate of sound energy transmitted in the specified direction through a unit area normalto this direction at the point considered. Unit: watt per square meter. Nit symbol: W/m2. Letter symbol: L1
SOUND INTENSITY LEVEL.Ten times the common logarithm (i.e., to the base 10) of a given sound intensity to a reference sound intensity of 1 picowatt per square. meter (10·12 W/m2). Unit: decibel. Unit Tt
Sound Spectrum A representation of the magnitude (e.g. amplitude and phase) of the components of a complex sound as a function of frequency.
Sound Transmission Class A single number rating used to compare the sound insulation properties of walls, floors, ceilings, windows, or doors. The sound transmission class is derived from measurements in 16 test bands. Abbr: STC.
Source Room A room that contains a noise source or sources.
Spectrum A description of a quantity as a function of frequency; the term may be used to signify a continuous range of components usually wide in extent, which have some common characteristics, such as the audio-frequency spectrum.
Speech Interference Level An index for assessing the interfering effects of noise on the intelligibility of speech, derived from measurements of background noise level of contiguous octave bands; i.e., the arithmetic average of the octave-band sound levels for the octave bands centered at frequencies of 500, 1000, 2000, and 4000 Hz (four-band method) or the corresponding average for the octave bands centered at 500, 1000, and 2000 Hz (three-band method). If other than octave bands are used, they must be specified. Unit: decibel. Unit symbol: dB. Abbr. SIL.
SOUND PRESSURE LEVEL, SPL In air, 20 times the. logarithm (to the base 10) of the given sound pressure to the reference sound pressure of 20 micropascals (mPa) Unit, Db, Symbol Lρ
STANDING WAVES Periodic waves having a fixed amplitude distribution in space resulting from interference of progressive waves of the same frequency and kind.
Static Pressure At a point in a medium, the pressure that would exist at tha1 point in the absence of sound waves. Unit: pascal. Uni1 symbol: Pa (1 Pa = newton per square meter= 10 dynes per square centimeter).
Static Regain The energy regained after tubular flow becomes laminar again
STC (Sound Transmission Class) A one number rating system of the overall transmission loss of a wall system (or blocking system)
Structure Borne Sound Sound that arrives at a point of interest by propagation through a solid structure.
Transmission Loss Of a partition, for a specified frequency band, the difference between the average sound pressure levels in the reverent source room and receiving room (expressed in decibels) plus 10 times the logarithm to the base 1 O of the ratio of the area of the common partition to the total Sabin absorption in the receiving room. Abbr: TL.
Wavelength Of a periodic wave in an isotropic medium, the perpendicular distance between the two wavefronts in which the displacements have a difference in phase of one complete period. Unit: meter. Unit symbol: m. Letter symbol: A
White Noise A sound whose power spectral density is essentially independent of frequency. {White noise need not be random noise).